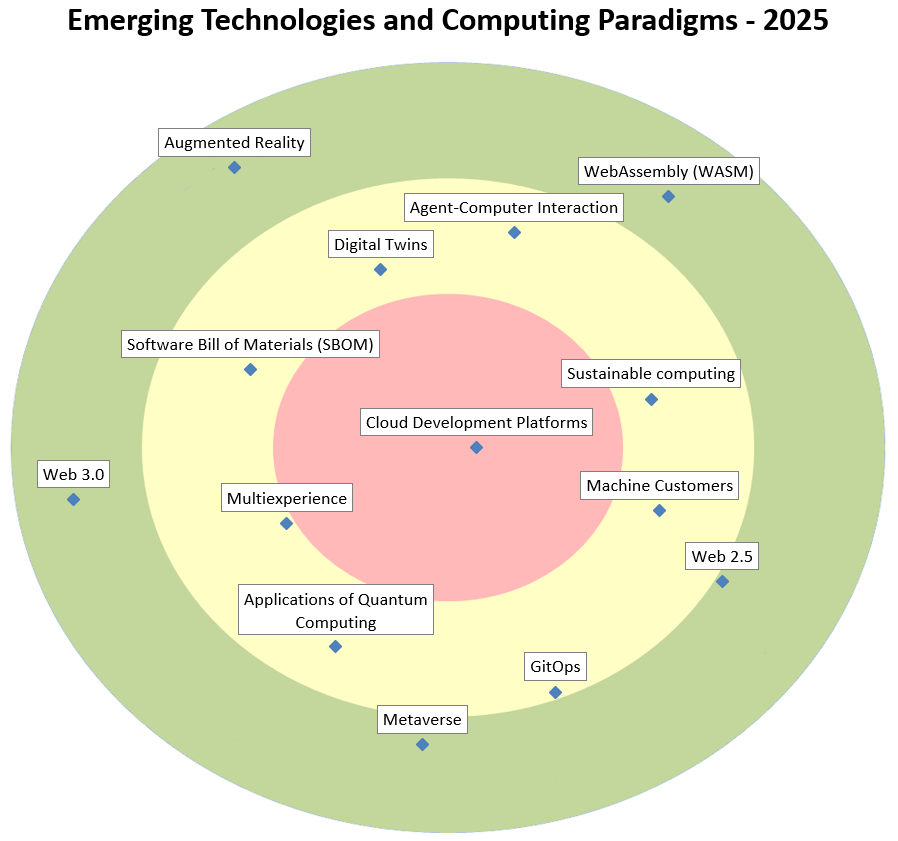
| Cloud Development Platforms | The traditional IDE is now often running in the Cloud, and accessed through the browser. The benefit is a greatly standardized environment, and the offloading of building and testing the software to more powerful servers instead of the developer’s laptop. It is also easier to secure the environment. | |
| Agent-Computer Interaction | Agent-Computer Interaction deals with the interplay between AI Agents and software user interfaces. An AI with agency over a user interface, can execute tasks by managing input and output as a human would, such as interpreting screens, controlling the mouse, and automating data entry. | |
| Sustainable computing | Sustainable computing also refer to as green computing is an approach to reduce the environmental impact of a computing system. It is an holistic approach that aims at using resources efficiently in all aspects of the system lifecycle, from the chip level to the application level and its usage. | |
| Machine Customers | More and more traffic to websites and APIs is driven by autonomous entities, often powered by AI. We call these machine customers. API and site builders should be prepared for this kind of traffic. | |
| GitOps | GitOps manages infrastructure by storing configuration in Git repositories. Changes are made through Git commits and automatically deployed. It ensures version control, auditability, and consistent deployments, enhancing reliability and collaboration. | |
| Applications of Quantum Computing | As quantum computers are getting more powerful, it becomes increasingly relevant to detect uses cases in the public sector where powerful quantum computers could have an added value. | |
| Multiexperience | Multiexperience is the seamless integration of various digital experiences, such as websites, mobile apps, AR/VR, and voice assistants, to provide a consistent and user-centric interaction across different devices and interaction modalities like text, language, voice, vision and gesture. | |
| Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) | SBOM is a comprehensive list of all software components, dependencies, and metadata used to build a software product. It provides transparency into the software supply chain, aiding in vulnerability management, license compliance, and security risk assessment. | |
| Digital Twins | Is a technology-enabled proxy that mirrors the state of a physical object or system e.g. an organization, building, network, device or even a person (citizen). It’s used to simulate, monitor, and optimize the real-world counterpart, enabling better decision-making and problem-solving. | |
| WebAssembly (WASM) | WASM is used to build high performance applications in the browser, and is becoming ever more versatile and powerful. One could imagine even AI browser applications working locally on a user’s machine. | |
| Web 2.5 | WEB 2.5 bridges Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 by integrating decentralized technologies like blockchain into existing platforms. It combines the familiar ease of use of Web 2.0 applications with the innovative and decentralized features of Web3. | |
| Metaverse | The metaverse is a virtual world where people can interact with each other and with digital objects in a 3D environment. It’s like a virtual reality internet, where you can socialize, work, and play. It uses a combination of virtual and augmented reality. | |
| Web 3.0 | Web 3.0 is an idea for the next generation of the internet, characterized by decentralization, user ownership, and blockchain technology. It aims to create a more open, secure, and user-centric web experience. | |
| Augmented Reality | Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing our perception. It uses devices like smartphones or AR glasses to blend virtual elements seamlessly with our surroundings. |